Qui aura 20 en maths ?
💯 Le grand concours 100% Terminale revient le 31 janvier 2026 à l'ESIEA Paris !Découvrir →
Nouveau
🔥 Découvre nos fiches d'exercices gratuites avec corrections en vidéo !Accéder aux fiches →
QCM Bilan Numéro 2 - Exercice 1
20 min
40
Question 1
Cet exercice est un questionnaire à choix multiples (QCM). Pour chacune des questions ci-dessous, une seule des réponses est exacte. Pour chaque question, vous devez bien sur justifier.
Soit la fonction définie sur par . La limite de en est égale à :
Correction
nous rencontrons une forme indéterminée de la forme
Au voisinage de et de un polynôme est équivalent à son monôme de plus haut degré.
Ce qui nous donne :Question 2
Soit la fonction définie sur par et sa courbe représentative. admet comme asymptote la droite d'équation :
Correction
on obtient une forme indéterminée
Au voisinage de et de un quotient de polynômes est équivalent au quotient des monômes de plus haut degré.
Il vient alors que :- Si où est une valeur finie alors la fonction admet une asymptote horizontale d'équation
- Si où est une valeur finie alors la fonction admet une asymptote horizontale d'équation
Question 3
Correction
Ainsi :
Question 4
Correction
On commence par calculer
Au voisinage de et de un polynôme est équivalent à son monôme de plus haut degré.
Ce qui nous donne :Ainsi :
On pose . Lorsque tend vers alors tend vers .
Or :
Par composition :
Question 5
Correction
que l'on peut aussi écrire
par quotient .
On peut expliquer le fait que de la manière suivante :
Nous avons dressé le signe de la fonction ci dessous :
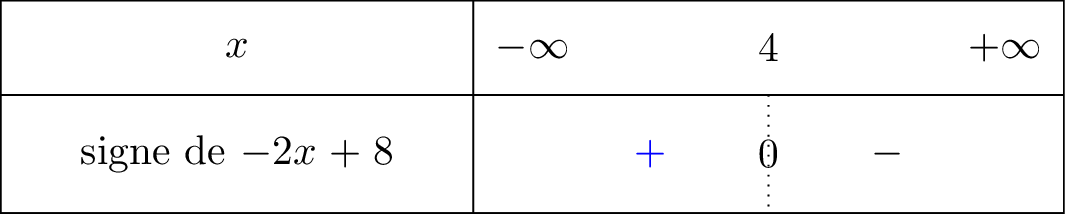 signifie que tend vers mais avec , donc lorsque on voit bien à l'aide du tableau de signe que nous sommes dans la partie positive. C'est pour cela que .
signifie que tend vers mais avec , donc lorsque on voit bien à l'aide du tableau de signe que nous sommes dans la partie positive. C'est pour cela que .
Nous avons dressé le signe de la fonction ci dessous :

, Ici on a le numérateur tend vers donc négatif et le dénominateur s'approche de de manière positive.
Le numérateur est négatif et le dénominateur positif donc le quotient tend vers .
Le numérateur est négatif et le dénominateur positif donc le quotient tend vers .
Question 6
Correction
Pour tout réel , on a :
équivaut successivement à :
, on va ensuite diviser par qui est strictement positif car nous sommes au voisinage de
D'après le théorème des gendarmes :
Si on rencontre une forme alors la limite sera égale à zéro.
Question 7
Correction
Pour tout réel , on a :
équivaut successivement à :
Attention, ici on n'applique pas le théorème des gendarmes car les limites ne sont pas des valeurs finies.
On va garder l'inégalité de droite, ce qui donne :
Comme et alors d'après le théorème de comparaison
Question 8
Correction
par quotient .
Interprétation graphique : la courbe admet une asymptote verticale d'équation .
On peut expliquer le fait que de la manière suivante :
Nous avons dressé le signe de la fonction ci dessous :
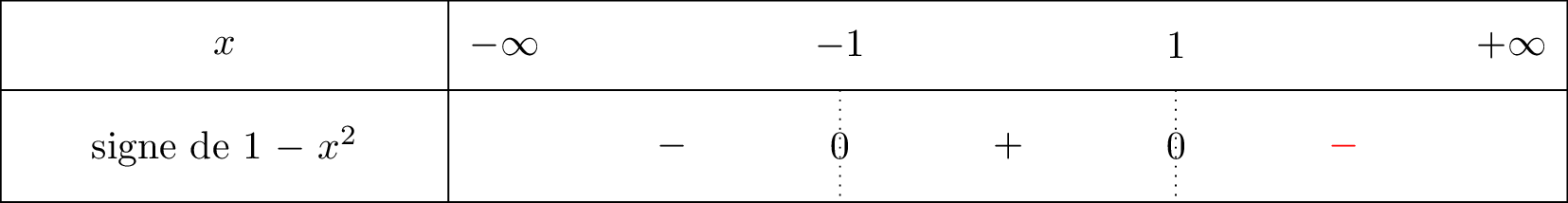 signifie que tend vers mais avec , donc lorsque on voit bien à l'aide du tableau de signe que nous sommes dans la partie négative. C'est pour cela que .
signifie que tend vers mais avec , donc lorsque on voit bien à l'aide du tableau de signe que nous sommes dans la partie négative. C'est pour cela que .
Nous avons dressé le signe de la fonction ci dessous :

. Ici on a le numérateur tend vers donc positif et le dénominateur s'approche de de manière négative.
Le numérateur est positif et le dénominateur est négatif donc le quotient tend vers .
Le numérateur est positif et le dénominateur est négatif donc le quotient tend vers .
Question 9
Correction
On commence par calculer .
Ainsi :
On pose . Lorsque tend vers alors tend vers .
Or :
Par composition :
Question 10
Correction
Question 11
Correction
Ainsi :
Signaler une erreur
Aide-nous à améliorer nos contenus en signalant les erreurs ou problèmes que tu penses avoir trouvés.
Connecte-toi ou crée un compte pour signaler une erreur.